BCSExplorer FAQ
1. Introduction:
We have developed a new available web application BCSExplorer. This web is the first web application of where compounds generation is integrated with biosynthesis analysis.
The main novel aspects of the web are the following:
- A comprehensive reaction database: The web constructs the most comprehensive biosynthesis database with 280 000 biochemical reactions reported worldwide over the past 130 years, which have been manually curated by more than 100 people from 562 430 published biosynthesis references.
- Redundant rule removal: A reaction rule merge algorithm to remove redundancy rules is presented in this study. As we know, prediction is a very time consuming step using transformations, which would be costlier for the increasing number of the reaction rules.
- Biosynthesis analysis: Various model synthesis analysis methods are used for all possible compounds analysis to meet the different needs of researchers, including biosynthesis feasibility, drug‑likeness and toxicity analysis.
The tool can result in a large number of molecules to be examined visually by a researcher to select the most interesting for further consideration. The web site will be useful in exploring biosynthetic chemical space.
2. Query Submitted:
The various opretors of input:
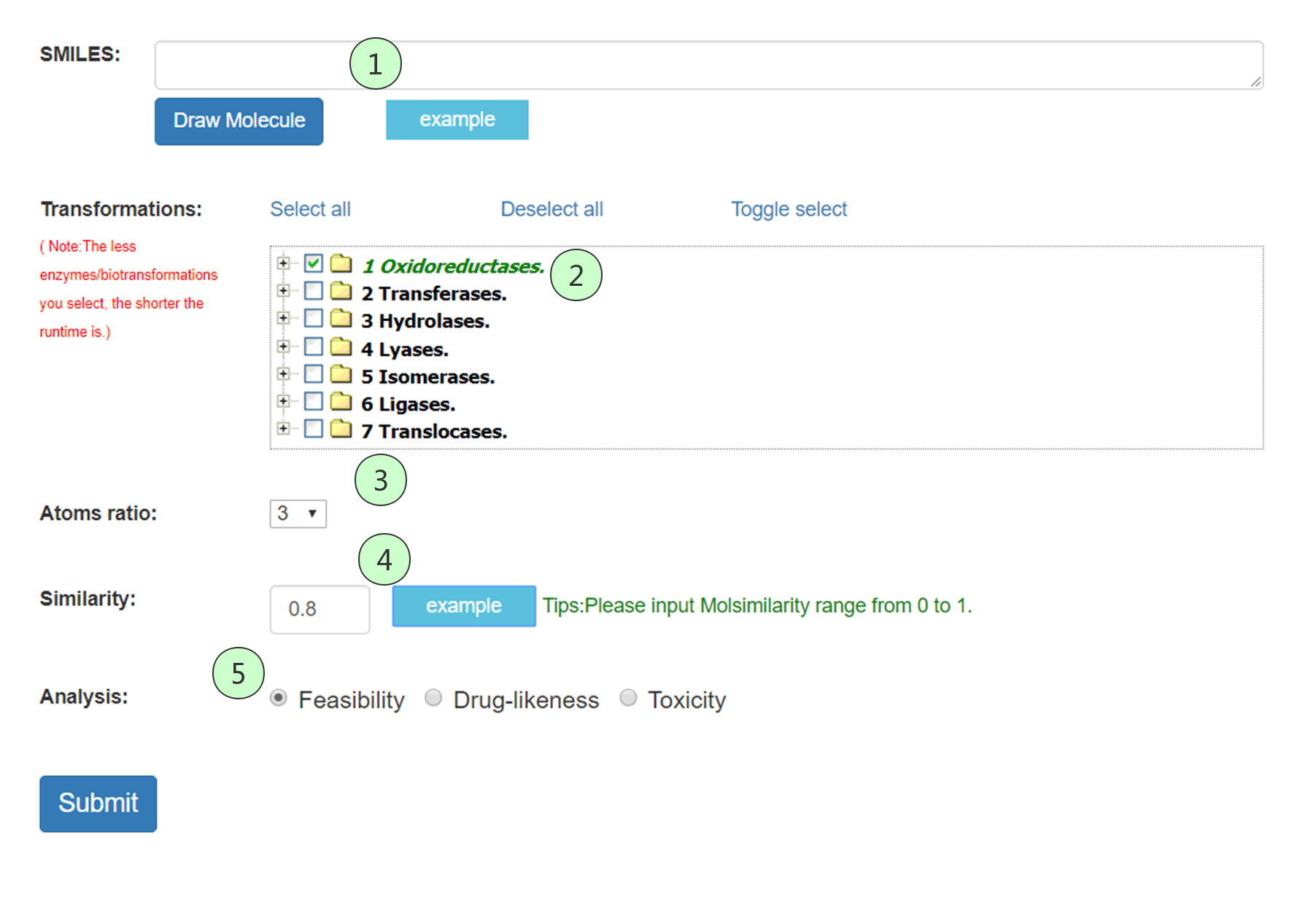
Fig 1 The search interface of BCSExplorer. (1) Smiles: The query compound can be represented as SMILES input by the user or drawn with a molecular input editor. (2) Transformations: A menu on the selection of transformations. (3) Atoms ration: The ratio of heavy atom count in the product compared to reactant. (4) Similarity: The similarity between query reactant and native reactant. (5) Analysis: biosynthesis feasibility, drug-likeness and toxicity analysis are used to assess all possible compounds to meet the different needs of researchers.
3. About search result
The results will be display as a tree in a few minutes in a new page after clicking the button “Submit” in BCSExplorer. An example on the synthesis tree is constructed using biosynthesis feasibility, as shown in Fig 2. In the synthesis tree, the root corresponds to the starting material; leaves represent the bio-derivatives which are ranked by synthetic accessibility (SA) score. A lower SA score is easier to synthesis. Compounds whose SA score is less than 5 will be colored in green, greater than 7 will be colored in red, and the rest will show in blue. When the cursor moves on the nodes, the related chemical structures will be shown. After right clicking the child node, choosing “Add New” button and selecting a list of operators, the user can obtain the next cycle results in a few minutes.
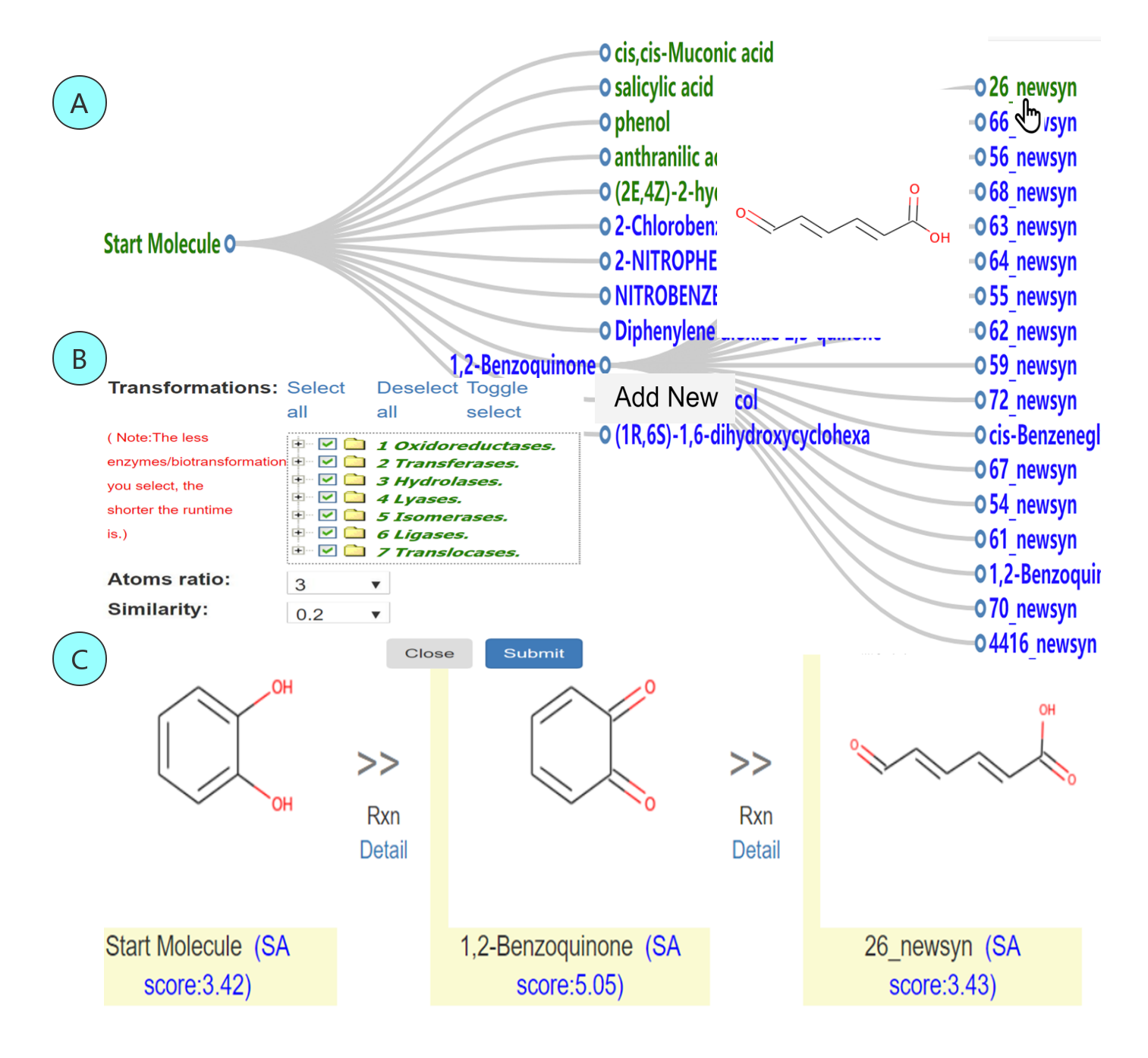
Fig 2 A An example of the synthesis tree generated from the start molecule. Tree child nodes are ranked by SAscore. The nodes marked with green are easy to synthesize. The edge is embedded with synthetic route from the root to the leaves. B Operators to the next generation of new compound structures after right clicking the tree node. C Traced synthetic route from the start molecule to the molecule in leaves. The detailed information at each step of an overall pathway is embedded in “Detail”.
After clicking ‘Detail’ in Fig 2, the below will list the details of the predicted reantion and reference biochemical reactions. An example is shown in Fig 3. The detailed biochemical reaction is displayed in Fig 4.
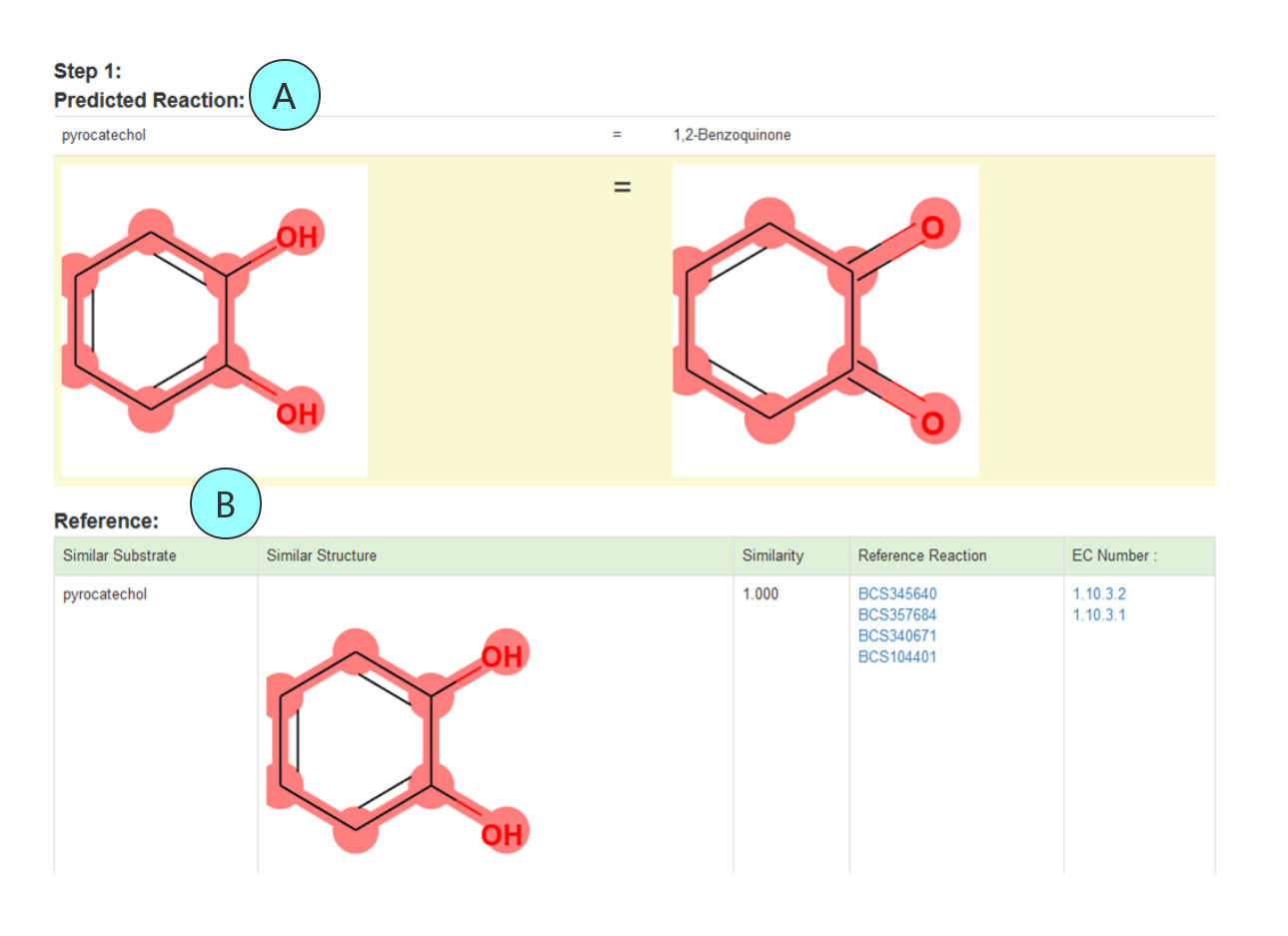
Fig 3 A The predicted reaction in which changed atoms are marked with red circles. B The reference reactions information by listing the molecular structure, the similarity between substrates, the reference biochemical reaction and the associated enzyme classfication.
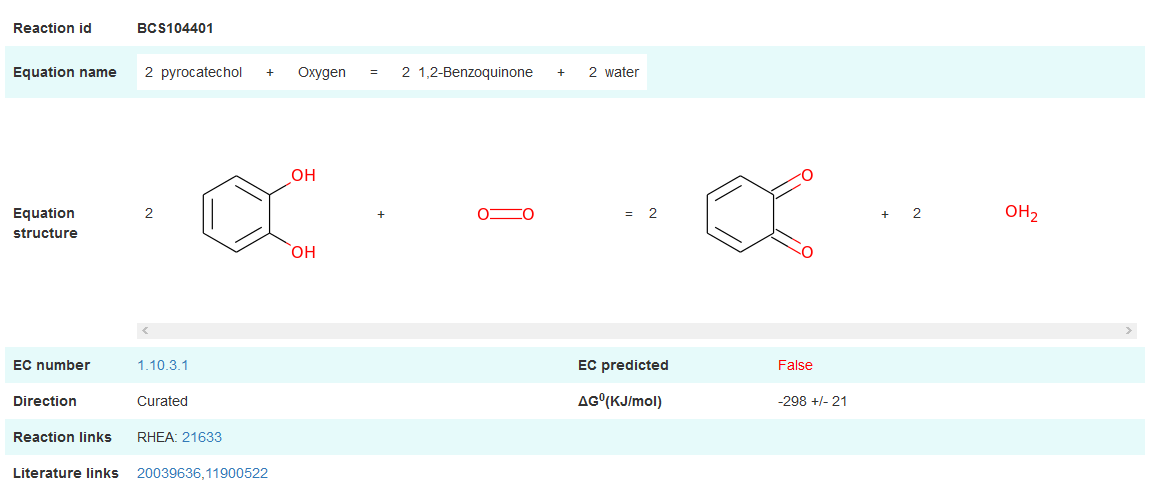
Fig 4 The detailed information of reference biochemical reaction. EC (Enzyme Commission) number is source from other database when "EC predicted" is False. It indicates that EC number is assigned by our method when "EC predicted" is True.
4. Privacy Policy
We don’t collect any personal information from our users.
While using our Site, there are two type of information you might provide to us: query molecule information and chemical predicted potentials collected by us as you interact with our websites. The information collected is used by BCSExplore for the purpose of providing you with the content you request. We do not share or disclose your information to third parties.
5. Contact us
When using BCSExplore, if you encounter any problem please contact RxnFinder Team.
Email: service@esynbio.com